Leave Your Message
The importance of safety in industrial settings cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to handling flammable materials. Tank flame arrestors play a crucial role in preventing the ignition of flammable vapors that can erupt from storage tanks. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), approximately 50% of fire incidents in industrial facilities are linked to the handling of combustible liquids and gases. Therefore, selecting the right tank flame arrestor is not just a regulatory requirement but a vital aspect of comprehensive safety management.
Industry data from various safety studies highlight that the implementation of tank flame arrestors can significantly reduce the likelihood of catastrophic incidents. The American Petroleum Institute (API) reports that proper flame arrestor systems can lower the risk of fire-related accidents by over 30%. This statistic underscores the necessity for facility managers and safety professionals to thoroughly assess their operational needs and the specific environments in which they operate. Choosing the correct tank flame arrestor requires an understanding of both the operational environment and the characteristics of the materials being stored, as each factor can dramatically influence the effectiveness of the safety device.
By taking an informed approach to the selection of tank flame arrestors, organizations can enhance their safety protocols and protect against potential disasters. As industrial environments continue to evolve, so too must the strategies surrounding fire prevention and risk management, making the informed choice of tank flame arrestors a non-negotiable component of workplace safety.

Tank flame arrestors play a crucial role in maintaining safety in environments where flammable vapors are present. These devices are designed to prevent flame propagation into storage tanks, reducing the risk of fire or explosion. By creating a barrier against external flames, tank flame arrestors protect not only the tank’s contents but also the surrounding infrastructure and personnel. Understanding the mechanisms and importance of these safety devices is essential for anyone involved in handling hazardous materials.
Selecting the appropriate tank flame arrestor involves careful consideration of its design and the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as the type of vapors being stored, the tank's size, and the environmental conditions all influence the effectiveness of the flame arrestor. A well-chosen flame arrestor not only enhances safety but also ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations. Investing in the right equipment is vital for maintaining a safe working environment and minimizing potential hazards associated with flammable materials.
When selecting a tank flame arrestor, understanding the various types available is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance with industry standards. The most common types of flame arrestors are those designed for use in venting applications, including passive and active systems. Passive flame arrestors utilize specially designed mesh and baffles to extinguish flames as they travel through the unit, making them ideal for storage tanks that handle flammable vapors. Their simplicity and low maintenance requirements make them a popular choice in many industries.
Active flame arrestors, on the other hand, employ mechanical features to enhance safety. These devices include flame detection and extinguishing mechanisms, providing an additional layer of protection. Active systems are particularly beneficial in environments where there is a risk of fast-transient ignitions or where process conditions can change rapidly. Additionally, some specialized flame arrestors are designed for specific applications, such as low-pressure systems or those with varying flow rates, ensuring that every safety need is accurately addressed. By understanding these differences, users can make informed decisions tailored to their specific safety requirements.
This chart illustrates the various types of tank flame arrestors used in safety applications, highlighting their frequency of use. The data demonstrates that traditional flame arrestors are the most commonly used, while other types are utilized less frequently, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right type for specific safety needs.
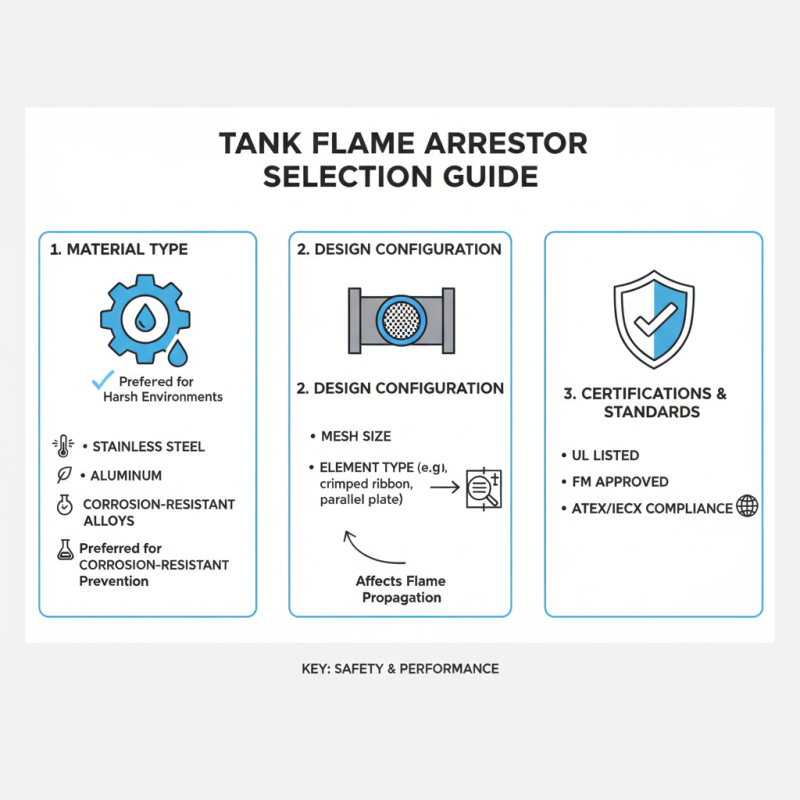
When selecting a tank flame arrestor, it's essential to focus on key features and specifications that directly impact safety and performance. One of the primary considerations is the type of material used in the construction of the flame arrestor. Options typically include stainless steel, aluminum, or other corrosion-resistant materials. Each has its advantages, but stainless steel is often preferred for environments exposed to corrosive elements or high temperatures. Additionally, consider the design of the flame arrestor; options include various mesh sizes and configurations that determine the device's effectiveness in preventing flame propagation.
Tips for choosing the right flame arrestor include evaluating the specific application and the type of flammable vapor or gas involved. Ensure the arrestor is rated for the substances you are handling and can withstand the associated pressures and temperatures. It's also vital to assess the maintenance requirements of the device; a flame arrestor should allow for easy inspection and cleaning without compromising safety.
Another critical specification is the flow rate capacity. Selecting an arrestor that can accommodate the maximum flow rate of your application will prevent pressure build-up and reduce the risk of operational failures. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines and ensure compliance with safety standards relevant to your industry.
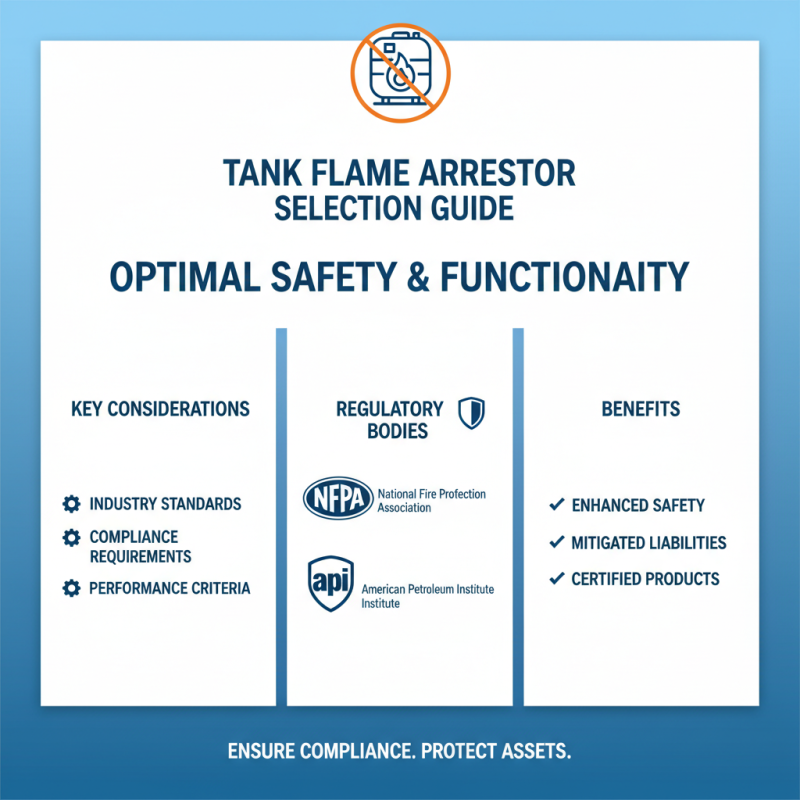
When selecting a tank flame arrestor, it's crucial to consider industry standards and compliance requirements to ensure optimal safety and functionality. Various industries have established specific regulations that define the performance criteria and testing methods for flame arrestors. Understanding these standards, such as those set by organizations like the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) or the American Petroleum Institute (API), can help you assess whether a product meets the necessary safety benchmarks for your application. Compliance with these standards not only enhances safety but also mitigates potential liabilities associated with non-compliance.
Additionally, it's important to acknowledge that different applications may require adherence to different standards. For example, fueling operations and chemical storage facilities may have distinct requirements based on the materials they handle and the environment in which they operate. Evaluating the specific operational risks and consulting the pertinent regulations will guide you toward making an informed decision. Always ensure that the chosen flame arrestor is not only compliant with local and national regulations but also certified for the specific conditions of your environment to guarantee robust protection against fire hazards.
When selecting a tank flame arrestor, assessing installation and maintenance needs is critical for ensuring optimal performance and safety. According to a 2022 report by the Fire Protection Research Foundation, improper installation can lead to a significant increase in fire hazards. The report notes that nearly 40% of industrial incidents related to flames arise from poorly installed safety equipment, underlining the importance of adherence to manufacturer guidelines and local regulatory standards. Proper installation involves evaluating the tank's design, the type of flammable substances handled, and the environmental conditions, such as temperature and pressure fluctuations.
Maintenance is equally paramount, as regular inspections can identify potential failures before they escalate into dangerous situations. Industry standards recommend that flame arrestors be inspected at least once a year; however, in high-risk environments, quarterly evaluations may be necessary. A study published in the Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries reveals that facilities performing routine maintenance on safety equipment have seen a reduction in incident rates by up to 30%. This highlights the importance of developing a maintenance schedule that includes not just visual inspections but also functional tests to ensure every component is operating as intended. By prioritizing installation and maintenance, businesses can significantly enhance their safety protocols and protect both personnel and property.
| Flame Arrestor Type | Installation Requirements | Maintenance Frequency | Recommended Applications | Performance Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Flame Arrestor | Simple installation, no power required | Annually | Storage tanks, pipelines | Up to 99% |
| Detonation Flame Arrestor | Requires specific configuration, may need skilled installation | Bi-annually | High hazard areas, distillation units | 95% - 99% |
| Vortex Flame Arrestor | Requires specific airflow considerations | Every 6 months | Chemical processing, vapor recovery | Up to 98% |
| Hybrid Flame Arrestor | Complex installation; may require electrical setup | Quarterly | Versatile applications, industrial processes | Up to 99.5% |